A neodymium magnet (also known as NdFeB, NIB or Neo magnet), the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet, is a permanent magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. neodymium magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnet commercially available. They have replaced other types of magnet in the many applications in modern products that require strong permanent magnets, such as motors in cordless tools, hard disk drives and magnetic fasteners.

Description
The tetragonal Nd2Fe14B crystal structure has exceptionally high uniaxial magnetocrystalline anisotropy (HA~7 teslas – magnetic field strength H in A/m versus magnetic moment in A.m2). This gives the compound the potential to have high coercivity (i.e., resistance to being demagnetized). The compound also has a high saturation magnetization (Js ~1.6 T or 16 kG) and typically 1.3 teslas. Therefore, as the maximum energy density is proportional to Js2, this magnetic phase has the potential for storing large amounts of magnetic energy (BHmax ~ 512 kJ/m3 or 64 MG·Oe). This property is considerably higher in NdFeB alloys than in samarium cobalt (SmCo) magnets, which were the first type of rare-earth magnet to be commercialized. In practice, the magnetic properties of neodymium magnets depend on the alloy composition, microstructure, and manufacturing technique employed.
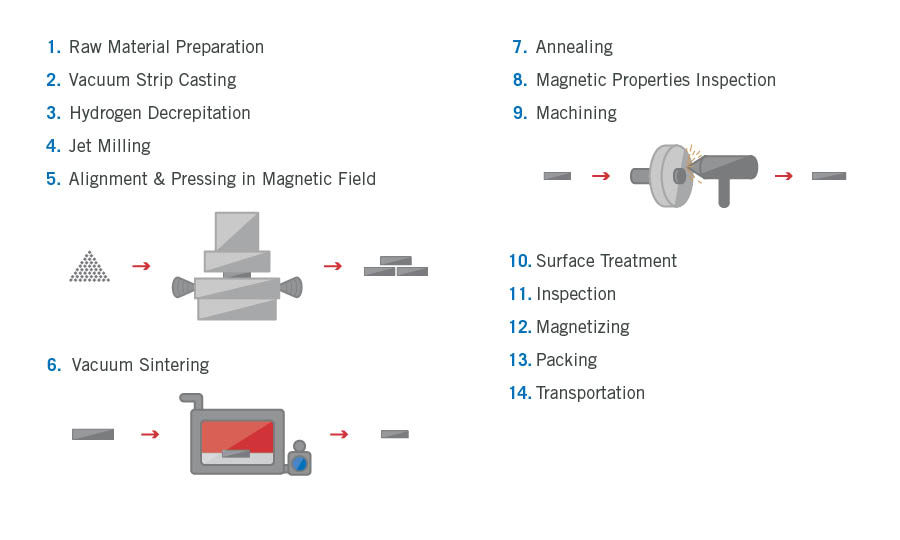
Production
The traditional forming method starts with large blocks of material to be cut into smaller blocks. In our proprietary process, the alloy material is first formed into a shape similar to the final product—thus reducing waste and cost. These savings we pass onto you, the customer.
Properties
Neodymium magnets are graded according to their maximum energy product, which relates to the magnetic flux output per unit volume. Higher values indicate stronger magnets and range from N35 up to N52. Letters following the grade indicate maximum operating temperatures (often the Curie temperature), which range from M (up to 100 degrees Celsius) to EH (200 degrees Celsius).

Grades of Neodymium magnets:
► N35-N52 176°F / 80°C
► 33M-48M 212°F / 100°C
► 30H-45H 248°F / 120°C
► 30SH-42SH 302°F / 150°C
► 30UH-42UH 356°F / 180°C
► 28EH-42EH 392°F / 200°C
| Grade | Remanence (BR) mT (KGS) |
Coercive Force (Hcb) kA/m (kOe) |
Intrinisc Coercive Force (Hcj) kA/m (kOe) |
Max. Energy Product (BH)max | Max. Operating Temp TW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N35 | 1170-1220 (11.7- 2.2) |
868 (10.9) |
955 12 |
263-287 (33-36) |
80 |
| N38 | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
899 (11.3) |
955 (12) |
287-310 (36-39) |
80 |
| N40 | 1250-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
907 (11.4) |
955 (12) |
302-326 (38-41) |
80 |
| N42 | 1280-1320 (12.8-13.2) |
915 (11.5) |
955 (12) |
318-342 (40-43) |
80 |
| N45 | 1320-1380 (13.2-13.8) |
923 (11.6) |
955 (12) |
342-366 (434-46) |
80 |
| N48 | 1380-1420 (13.8-14.2) |
923 (11.6) |
955 (12) |
366-390 (46-49) |
80 |
| N50 | 1400-1450 (14-14.5) |
796 (10) |
876 (11) |
382-406 (48-51) |
80 |
| N52 | 1430-1480 (14.3-14.80) |
796 (10) |
876 (11) |
398-422 (50-53) |
80 |
In addition to the above standard grades, there are 32 different high temperature grades of neodymium magnets available with a maximum operating temperature of up to 230 degrees Celsius. To give a neodymium magnet a greater resistance to being demagnetised at higher temperatures, varying levels of rare earth elements are used, typically resulting in a trade off with overall magnetic strength.
| Grade | Remanence (BR) mT (KGS) |
Coercive Force (Hcb) kA/m (kOe) |
Intrinisc Coercive Force (Hcj) kA/m (kOe) |
Max. Energy Product (BH)max | Max. Operating Temp TW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N33M | 1130-1170 (11.3-11.7) |
836 (10.5) |
1114 (14) |
247-263 (31-33) |
100 |
| N35M | 1170-2220 (11.7-12.2) |
868 (10.9) |
1114 (14) |
263-287 (33-36) |
100 |
| N38M | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
899 (11.3) |
1114 (14) |
287-310 (36-39) |
100 |
| N40M | 1250-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
923 (11.6) |
1114 (14) |
302-326 (38-41) |
100 |
| N42M | 1280-1320 (12.8-13.2) |
995 (12) |
1114 (14) |
318-342 (40-43) |
100 |
| N45M | 1320-1380 (13.2-13.8) |
995 (12.5) |
1114 (14) |
342-366 (43-46) |
100 |
| N48M | 1360-1430 (13.6-14.3) |
1027 (12.9) |
1114 (14) |
366-390 (46-49) |
100 |
| N50M | 1400-1450 (14.0-14.5) |
1033 (13) |
1114 (14) |
382-406 (48-51) |
100 |
| N35H | 1170-1220 (11.7-12.2) |
868 (10.9) |
1353 (17) |
263-287 (33-36) |
120 |
| N38H | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
899 (11.3) |
1353 (17) |
287-310 (36-39) |
120 |
| N40H | 1250-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
923 (11.6) |
1353 (17) |
302-326 (38-41) |
120 |
| N42H | 1280-1320 (12.8-13.2) |
955 (12) |
1353 (17) |
318-342 (40-43) |
120 |
| N45H | 1320-1360 (13.2-13.6) |
963 (12.1) |
1353 (17) |
342-366 (43-46) |
120 |
| N48H | 1370-1430 (13.7-14.3) |
995 (12.5) |
1353 (17) |
366-390 (46-49) |
120 |
| N35SH | 1170-1220 (11.7-12.2) |
876 (11) |
1592 (20) |
263-287 (33-36) |
150 |
| N38SH | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
907 (11.4) |
1592 (20) |
287-310 (36-39) |
150 |
| N40SH | 1240-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
939 (11.8) |
1592 (20) |
302-326 (38-41) |
150 |
| N45SH | 1320-1380 (13.2-13.8) |
1003 (12.6) |
1592 (20) |
242-366 (43-46) |
150 |
| N28UH | 1020-1080 (10.2-10.8) |
764 (9.6) |
1990 (25) |
207-231 (26-29) |
180 |
| N30UH | 1080-1130 (10.8-11.3) |
812 (10.2) |
1990 (25) |
223-247 (28-31) |
180 |
| N33UH | 1130-1170 (11.3-11.7) |
852 (10.7) |
1990 (25) |
247-271 (31-34) |
180 |
| N35UH | 1180-1220 (11.8-12.2) |
860 (10.8) |
1990 (25) |
263-287 (33-36) |
180 |
| N38UH | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
876 (11.0) |
1990 (25) |
287-310 (36-39) |
180 |
| N40UH | 1240-1280 (12.5-12.8) |
899 (11.3) |
1990 (25) |
302-326 (38-41) |
180 |
| N28EH | 1040-1090 (10.4-10.9) |
780 (9.8) |
2388 (30) |
207-231 (26-29) |
200 |
| N30EH | 1080-1130 (10.8-11.3) |
812 (10.2) |
2388 (30) |
223-247 (28-31) |
200 |
| N33EH | 1130-1170 (11.3-11.7) |
876 (10.5) |
2388 (30) |
247-271 (31-34) |
200 |
| N35EH | 1170-1220 (11.7-12.2) |
876 (11.0) |
2388 (30) |
263-287 (33-36) |
200 |
| N38EH | 1220-1250 (12.2-12.5) |
899 (11.3) |
2388 (30) |
287-310 (36-39) |
200 |
| N28AH | 1040-1090 (10.4-10.9) |
787 (9.9) |
2624 (33) |
207-231 (26-29) |
230 |
| N30AH | 1080-1130 (10.8-11.3) |
819 (10.3) |
2624 (33) |
223-247 (28-31) |
230 |
| N33AH | 1130-1170 (11.3-11.7) |
843 (10.6) |
2624 (33) |
247-271 (31-34) |
230 |
Coating necessary
Plating neodymium magnets is an important process to protect the magnet against its working environment. Below is a list of platings and their response to certain environments in regards to corrosion, durability, glueability, thickness, and price.
Plating Neodymium magnets is an electrolytic based process and can not be done after the magnet has been magnetized or "charged". All Neodymium Iron Boron magnets mused be plated to avoid oxidization.
Comparison of coating performance
| Surface treatment | Type | Typical thickness | Color | Remarks | Recommended max. temperature |
| Nickel coating | Ni+NI |
10-20 µm |
Silver (semi bright) | Excellent resistance to humid atmosphere |
200°C
|
| Ni+Cu+NI | superior resistance to humid atmosphere | ||||
| Zinc coating | Blue Zn | 8-20 µm | Silver blue | Good resistance to salt spray |
160°C |
| Color Zn | Excellent resistance to salt spray | ||||
| Tin coating | Ni+Cu+Sn | 15-20 µm | Silver semi bright | superior resistance to humid atmosphere | 160°C |
| Cupper coating | Ni+Cu | 10-20 µm | Gold shining | Temporary treatment | |
| Epoxy | Ni+Cu+epoxy | 15-25 µm | black | Excellent climatic and salt spray resistance |
120°C |
| Single epoxy | |||||
| Chemical coating | Ni | 10-20 µm | Silver semi bright | Excellent resistance to humid atmosphere | |
| Passivation | 0.1-0.3 µm | Silver gray | Temporary protection | 240°C |
Types of plating for magnets
| Element symbol | Name of element | φ10mm×10mm | Properties | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3CrZn |
Trivalent chromium zinc |

|
Chromate treatment. Recently hexavalent chromium has been regulated as an environmentally destructive substance and replaced with trivalent chromium |
|
| Ag | Silver |

|
Silver has the best electric conductivity out of all the metals, low contact resistance and good solderability but is easy to discolor. |
|
| Au | Gold |

|
Gold has good corrosion and oxidation resistance along with low electrical resistance. |
|
| Cr | Chrome |

|
Chrome has good abrasion and oxidation resistance and will not lose its shine in the atmosphere. |
|
| Cu | Copper |

|
Copper is easy to discolor so is used as a base. It is used to fill in dents and bring out a shine. |
|
| Ni | Nickel |

|
Nickel is chemically stable and has good anti-rust properties. It can be used for a wide range of purposes and is used as a base for gold plating, chrome plating etc. It can cause skin irritation. |
|
| NiBlack | Black nickel |

|
Black nickel is an alloy plating made of nickel, zinc and sulphur. The color may vary depending on the type of plating used as a base. |
|
| Sn | Tin |

|
Tin has excellent anti-corrosion properties and does not oxidize easily. It does not lose its shine easily and is safe to use in foods. |
|
| Rh | Rhodium |

|
Rhodium has excellent anti-corrosion properties and does not oxidize easily. It does not lose its shine easily and is safe to use in foods. |
|
| - | Un-treated |

|
No surface treatment coating. Rust will develop easily on neodymium magnets. |